Choosing the right welding machine is an essential decision for anyone involved in metalworking, whether you're a professional welder or a DIY enthusiast. With numerous options on the market, it can be challenging to know where to start. This article will answer basic questions and guide you through the essential factors to consider before buying a welding machine, ensuring that your purchase fits your needs, budget, and skill level.
1. What Type of Welding Do You Need?
Welding machines come in different types depending on the welding process. The most common types are Stick, MIG, and TIG welders. Each type has its own benefits and is suited to specific tasks:
Stick Welding: Ideal for heavy-duty welding in outdoor or windy environments. It’s a simple and robust option for working on thick materials.
MIG Welding: Known for its ease of use, MIG welding is perfect for beginners and is commonly used in light to medium fabrication work. It offers faster welding speeds and cleaner welds.
TIG Welding: This is the most precise type of welding, making it ideal for intricate work on thin materials. It requires more skill but results in high-quality, clean welds.
Determining the type of welding you intend to do is the first step in narrowing down your options. Consider the materials you plan to weld and the type of projects you’ll be working on.
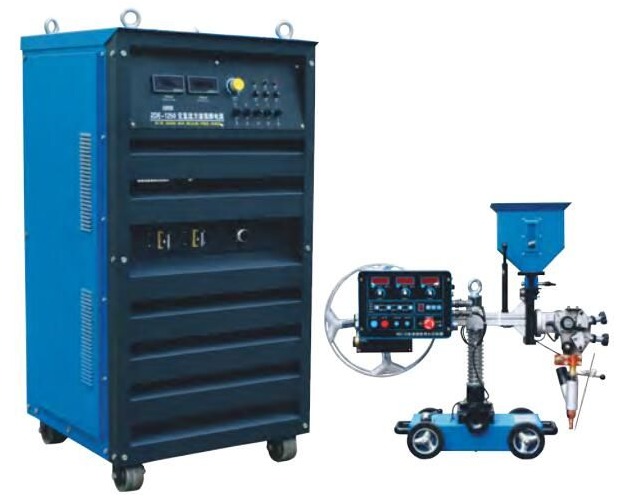

Automatic AC/DC Submerged Arc Welding Machine
2. What Is Your Welding Experience?
Your experience level plays a significant role in choosing the right welding machine. If you’re a beginner, you’ll want a machine that is easy to use, such as a MIG welder, which generally offers user-friendly controls and faster learning curves. For those with more experience, a TIG welder might be ideal, as it allows for greater precision and versatility.
If you’re new to welding, it’s advisable to opt for a machine that comes with clear instructions, safety features, and adjustable settings to accommodate different skill levels. Many machines also offer “auto-set” technology, which automatically adjusts settings based on the material you’re welding.
3. What Materials Are You Welding?
The material you plan to weld will affect the type of welding machine you should buy. Different machines are optimized for different materials:
Steel and Stainless Steel: Most welding machines can handle these materials, but MIG and Stick welders are typically the best options for steel welding.
Aluminum: Aluminum requires a machine that offers precise heat control, making TIG welding the best choice for aluminum work.
Cast Iron: Stick welding is often the go-to for welding cast iron due to its ability to work with thicker, tougher materials.
Before making your decision, ensure that the welder you choose is compatible with the materials you'll be working with most often. Some welding machines come with additional features or accessories specifically for aluminum or other specialized materials.
4. What Power Source Is Available?
Welding machines can be powered by either AC (Alternating Current), DC (Direct Current), or both. Each power source has different benefits depending on your needs:
AC Power: Often used in Stick welding, AC is ideal for general-purpose work, especially with thicker materials.
DC Power: DC power is preferred for TIG and MIG welding because it produces a more stable arc, making it easier to control the weld.
In addition to the power source, consider the machine’s voltage and amperage capabilities to ensure it meets your project’s requirements. Some machines are dual-voltage, which provides more flexibility when working in different locations or with various power supplies.
5. What Is Your Budget?
Welding machines come in a wide price range, from budget-friendly models for home use to high-end industrial machines. While it may be tempting to choose the cheapest option, it’s important to strike a balance between cost and quality. High-quality welders tend to last longer, provide better performance, and require fewer repairs over time.
It’s worth investing in a reliable, well-built machine if you plan to do extensive welding or need to rely on the welder for professional work. However, if you're just starting out or only need a welder for occasional use, you might be able to find a more affordable model that suits your needs.
6. What Features Should You Look for in a Welding Machine?
Modern welding machines come with a variety of features that can enhance usability and performance. Some of the most important features to consider include:
Adjustable Settings: Look for a machine that allows you to adjust the voltage, amperage, and wire speed to suit different welding applications.
Portability: If you need to move the welder frequently, choose a lightweight and portable machine. Some models even offer compact designs with wheels for easy transport.
Duty Cycle: This refers to how long the welder can run at a specific power output before needing to cool down. A higher duty cycle is better for longer welding sessions.
Safety Features: Features such as thermal overload protection, arc force control, and anti-stick technology can make your welding experience safer and more efficient.
Make sure to check the product specifications to ensure the machine you choose has the right features for your welding needs.
7. What Is the Brand’s Reputation?
When buying a welding machine, always consider the reputation of the brand. Established brands are more likely to offer reliable machines with good customer service and warranty options. Research customer reviews and ratings to learn about the experiences of others who have used the product you're considering.
Top brands typically offer better quality control, longer warranties, and more accessible customer support, which can be crucial in case you run into any issues with the machine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How much should I spend on a welding machine?
A1: The price of a welding machine depends on the type, features, and brand. Beginner machines can start at a few hundred dollars, while high-end models may cost several thousand. It’s important to balance your budget with your needs.
Q2: What is the best welding machine for beginners?
A2: MIG welders are typically the best choice for beginners due to their ease of use and versatility. They offer quicker learning curves and cleaner welds, making them ideal for those just starting out.
Q3: Can a welding machine be used for all metals?
A3: While most welding machines can handle a variety of metals, specific machines work better with particular materials. For example, TIG welding is preferred for aluminum, while MIG and Stick welders are better for steel.
Q4: What is the duty cycle of a welding machine?
A4: The duty cycle refers to how long the welder can operate without overheating. A 60% duty cycle means the machine can weld for 6 minutes out of every 10 minutes of use. A higher duty cycle is preferred for longer jobs.
Q5: How do I maintain my welding machine?
A5: Regular maintenance includes cleaning the machine, checking for wear and tear, replacing consumables like electrodes or welding wire, and ensuring proper ventilation to avoid overheating.
Do you want to receive more information about welding machines? Then we are happy to answer your questions. Fill in the contact form or send an email to https://www.sino-welding.com.